India is a vast and diverse country with hundreds of languages spoken by people throughout the subcontinent. While Hindi is the official language of India, the Indian Constitution recognizes 22 additional languages as "official" or "national" tongues. In this blog article, we will look at the languages spoken by Indians and why they are essential to Indian culture and identity. We'll explore whether regional dialects influence understanding amongst Indian tribes, how many individuals are bilingual or multilingual in India, and how knowing more than one language can benefit anyone living here.
Introduce the concept of language diversity in India
India is a linguistically diverse nation, with an astounding number of languages spoken across its length and breadth. The constitution of India recognizes 22 scheduled languages, which are divided into 5 language families: Indo-Aryan (spoken by 74% of the population), Dravidian (spoken by 24%), Austroasiatic (spoken by 1.3%), Sino-Tibetan (spoken by 0.6%) and a few minor language groups such as Nihali, Khasian, Burushaski etc., along with innumerable dialects and tribal languages.
These languages vary significantly regarding their geographical spread, linguistic features, socio-economic status, and speaker numbers. Of the total 92 documented languages, there are 14 languages with more than 10 million speakers and 32 languages with more than 1 million speakers, while the remaining have much smaller populations. Language diversity is also reflected in India's cultural landscape; many different customs, beliefs, rituals, festivals, etc., are bound together by a shared history and culture.
The language diversity of India is one of its most cherished characteristics, and the constitution has made great efforts to preserve it. It guarantees every citizen the right to use whichever language they prefer for educational or other official purposes, although Hindi remains the official national language. This linguistic diversity reflects the vibrant cultural fabric of India and serves as a reminder that incredible things can be achieved when people from different backgrounds come together in harmony.
India's language diversity is a testament to the resiliency and strength of its culture. It serves as a reminder that cooperation and understanding between different people, cultures, and languages can create something more significant than the sum of its parts. India stands united in celebrating its linguistic heritage through mutual respect and appreciation for each other's differences.
Understanding the Official Language of India
Hindi, written in Devanagari script, is the official language of India. English had been used as the official language during British rule, but after India regained its Independence in 1947, Hindi was declared the official language by the Indian Constitution on 26th January 1950. It was decided that English would be used alongside Hindi for another 15 years to ensure a smooth transition from English to Hindi. However, this period was extended several times, and even today, both languages are used officially throughout India.
At present, there are 22 scheduled languages recognized under the 8th Schedule of the Indian Constitution: Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia (formerly known as Oriya), Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, and Urdu. Hindi is the primary official language of the union, while English remains an associate official language for communication between states or the Central Government.
In India today, most citizens are bilingual in Hindi and English. The ability to speak both languages has enabled Indians to interact and communicate effectively with each other across different cultural backgrounds and contexts. It is this linguistic diversity that makes India genuinely unique!
The government has also taken specific measures to promote and preserve these languages, such as giving financial assistance to states for the development of their respective languages, setting up institutes and bodies like Kendriya Hindi Sansthan, Central Institute of Indian Languages (CIIL) and the National Council for Promotion of Urdu Language.
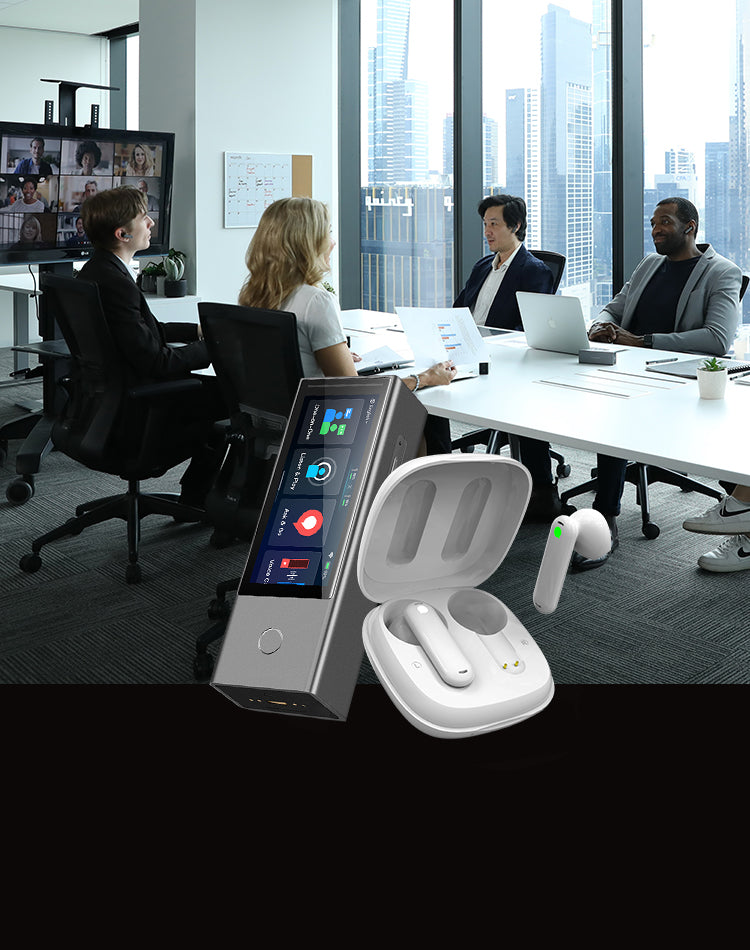
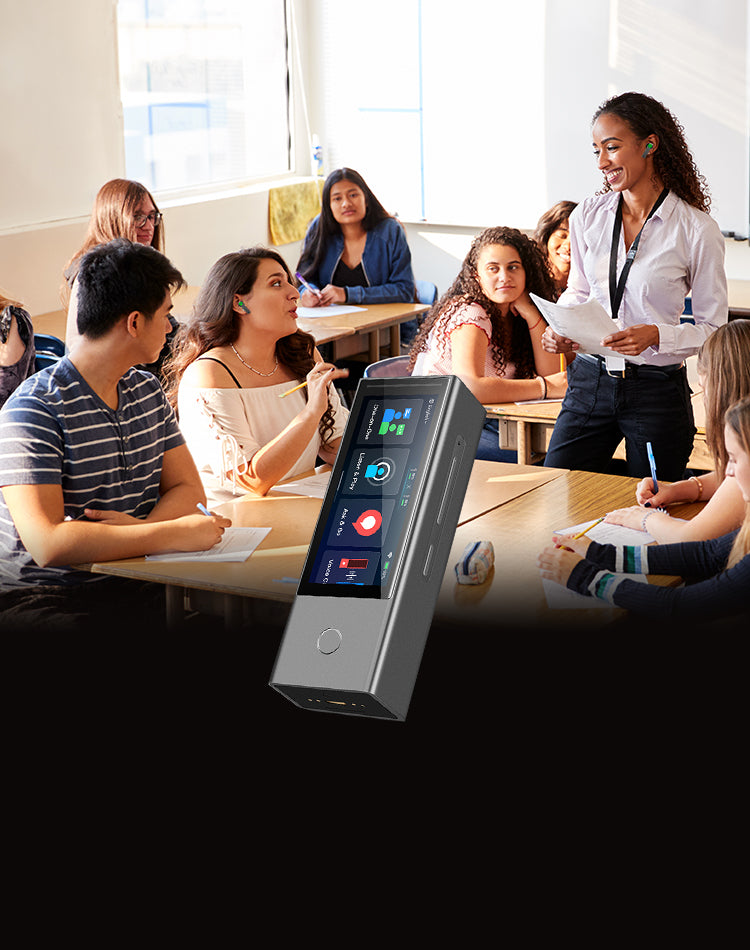
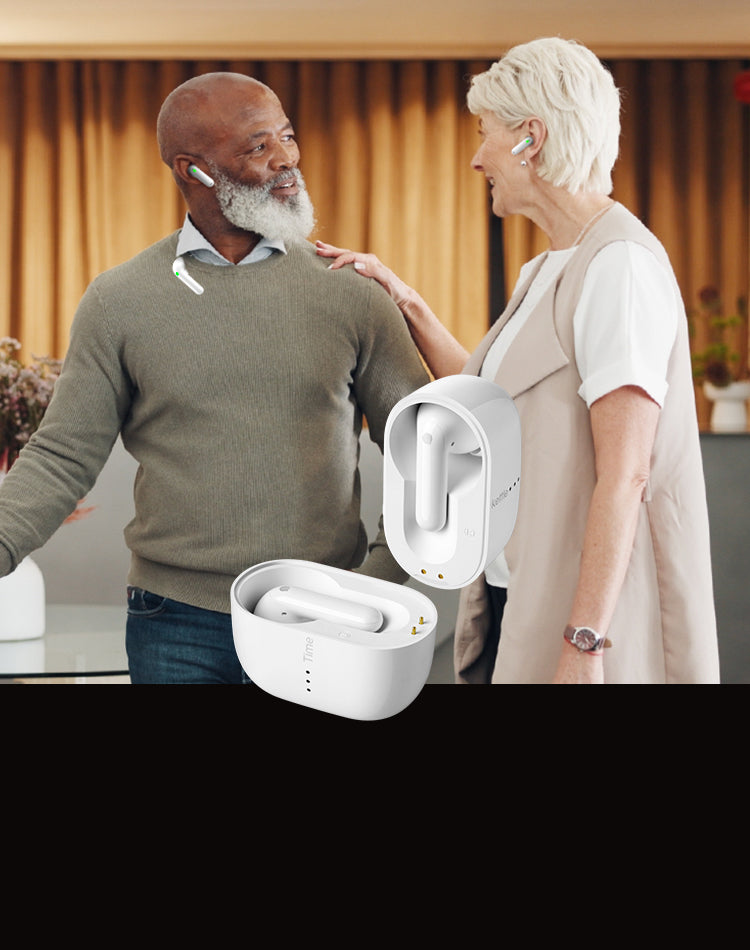
What are the benefits of using language translating earbuds in India?
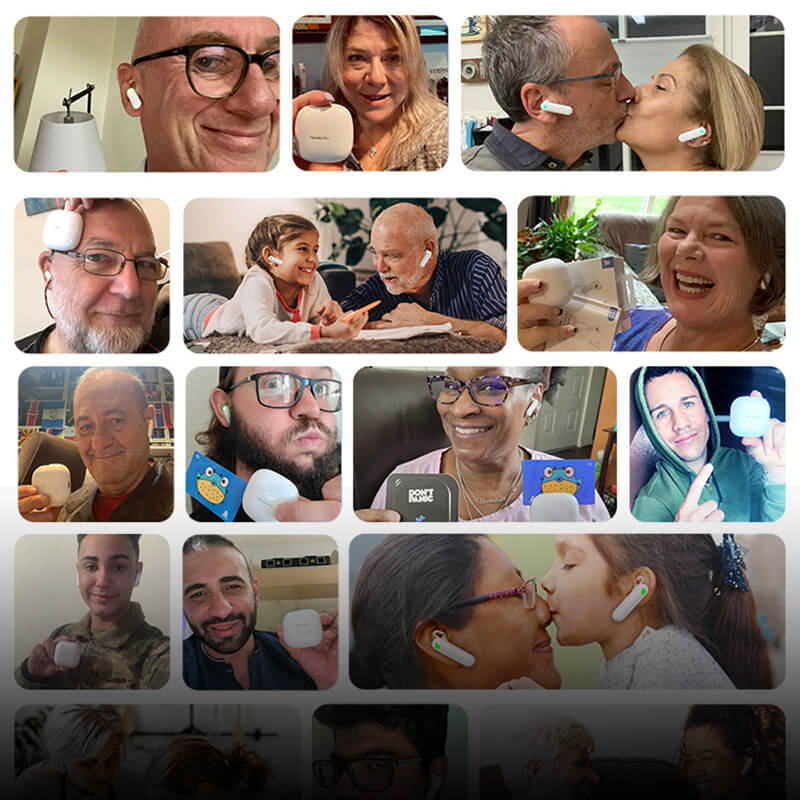
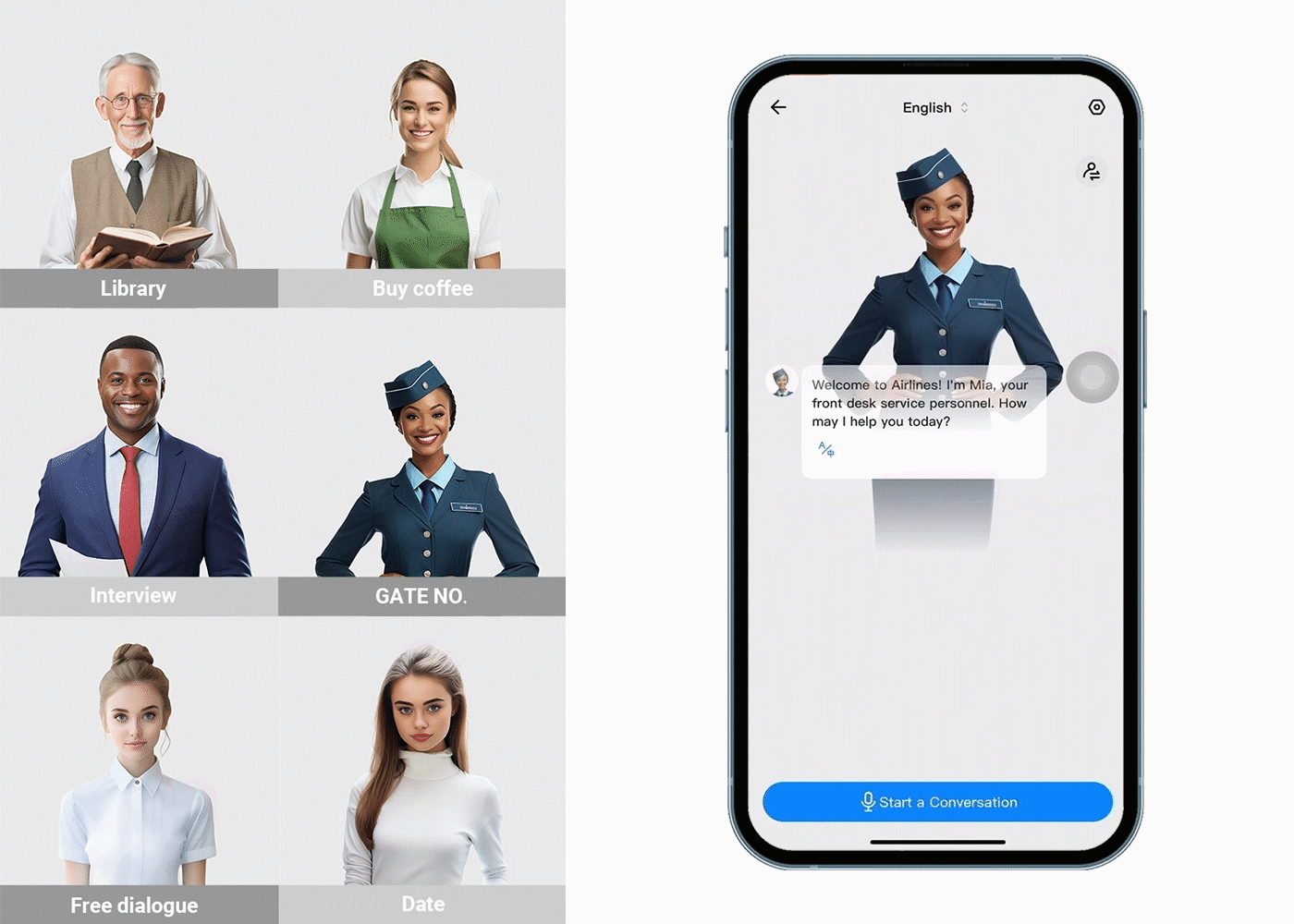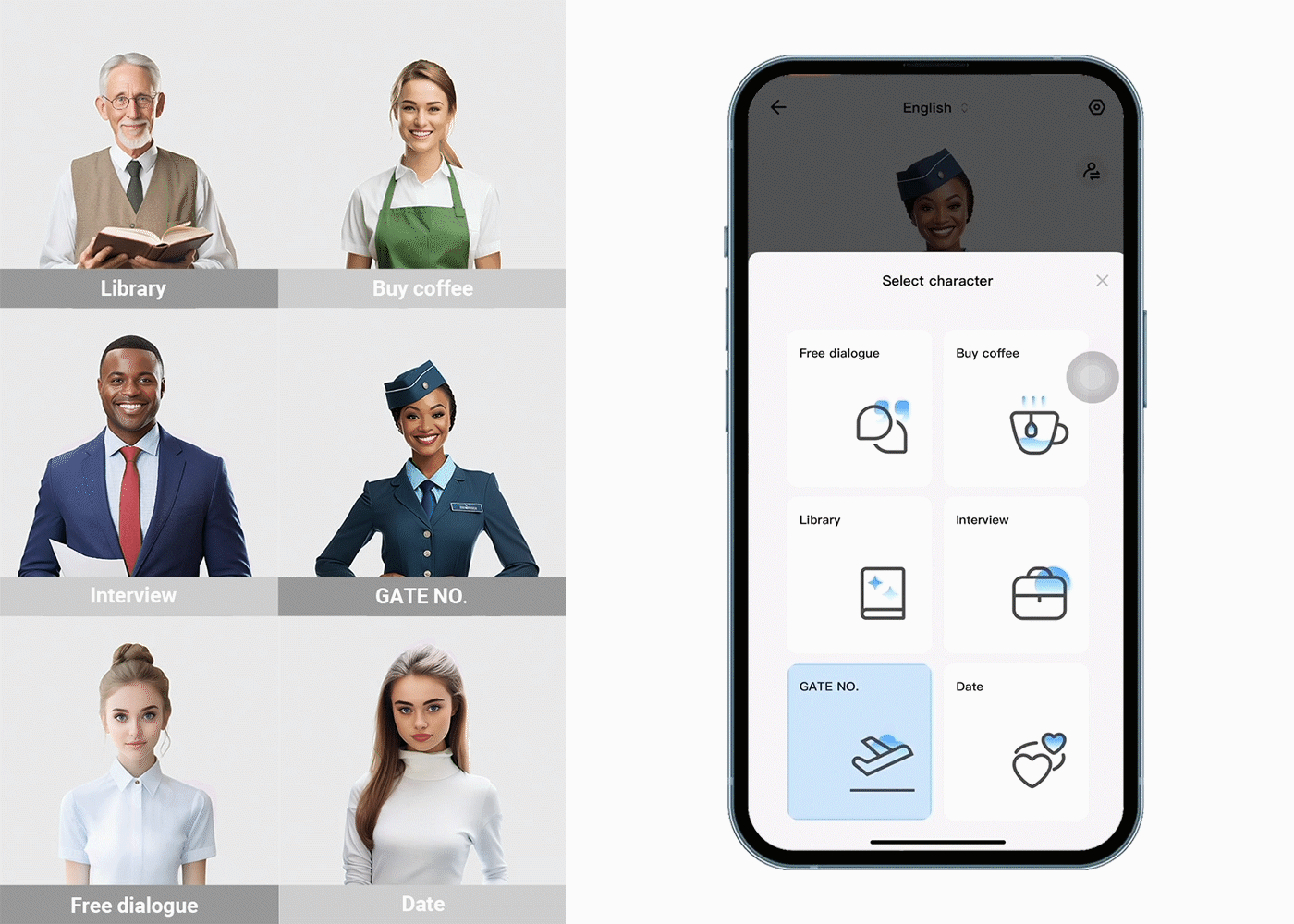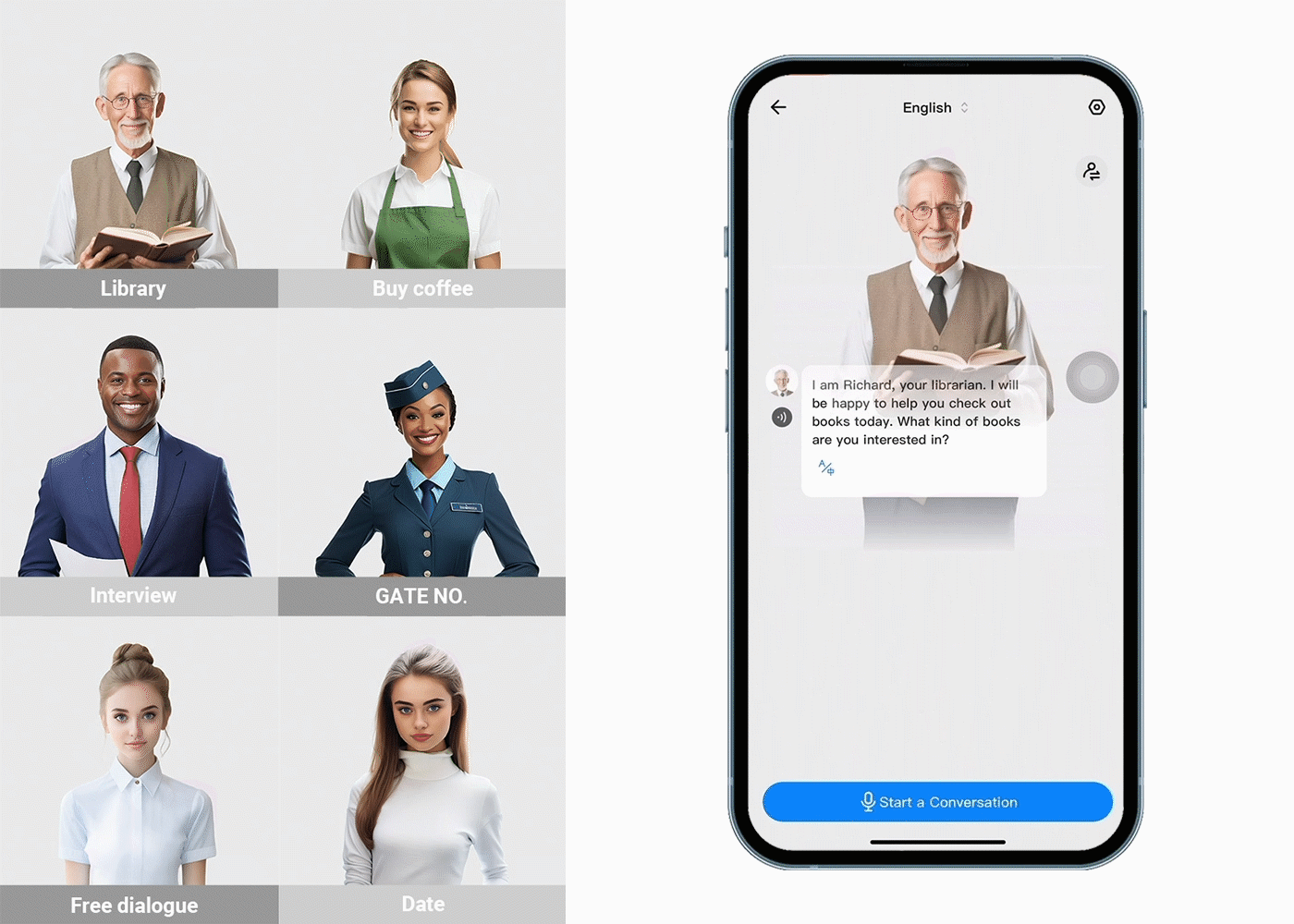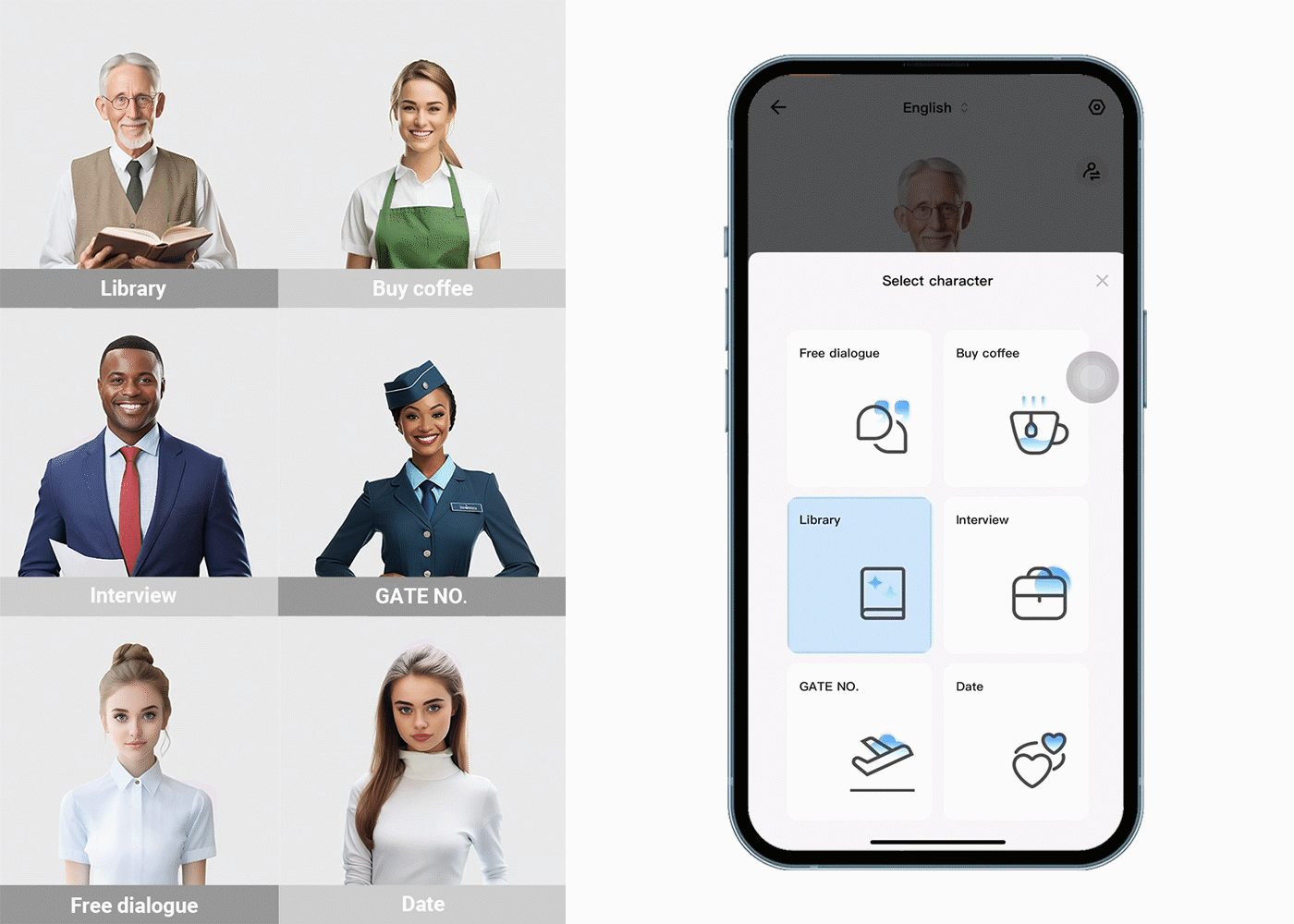
Language Translation Earbuds provide people with a unique and cost-effective way to communicate in multiple languages. For those traveling abroad or for foreigners entering India, language translation earbuds can be a huge help. Here are ten benefits of using Language Translation Earbuds for people:
- Real-time conversations in your native language while others speak another language.
- Easy to use and operate – no need to have extensive knowledge of the language you're trying to understand.
- Supports translations in 40+ languages, including Hindi and English, making it easier to get around without worrying about understanding foreign dialects.
- Structured grammar recognition technology allows users to relay their messages accurately to anyone of any language.
- Its portable and lightweight design makes it easy to carry, perfect for traveling or business trips.
- Hands-free operation allows users to keep their hands free while communicating in multiple languages.
- High-resolution audio delivers crystal clear sound quality even in noisy environments.
- It's a great way to learn a new language – the earbuds offer real-time translations that make learning easier and more enjoyable for any language learner!
- Connectivity options such as Bluetooth make syncing devices quick and easy - ensuring you never miss a meaningful conversation again!
- Its low power consumption ensures longer battery life, allowing users to use it for long periods without worrying about charging.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Which language is mainly spoken in India?
The most commonly spoken language in India is Hindi, which is spoken by over 40% of the population. Other widely used languages include Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, and Tamil.
What are the top 5 Indian spoken languages?
India's top 5 spoken languages are Hindi, Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, and Tamil. These five languages cover around 85 percent of the population of India.
What is the first language in India?
Sanskrit is considered to be the oldest language in India. It has been used for centuries by scholars and priests as a medium for religious texts and scriptures. Even though it is not widely spoken today, it still serves as a source of linguistic unity between many Indian languages.
Is it difficult to learn Hindi?
Hindi can be difficult to learn, especially for English speakers unfamiliar. However, with practice and dedication, anyone can become proficient in Hindi. Timekettle Translator earbuds are a great tool to help you learn Hindi faster and more effectively.
Conclusion:
Finally, Timekettle's Language Translation Earbuds offer a unique and convenient solution to language barriers in India. The ability to communicate in two or more languages in real-time makes it easier for Indians and foreigners to communicate. With advanced speech recognition technology, the earbuds make it effortless to understand different languages while still staying true to each person's native tongue. This is an invaluable tool for anyone who needs help crossing the language barrier in India.
 Talk to Customer Service 1(833) 491-1328
Talk to Customer Service 1(833) 491-1328











































发表评论
所有评论在发布前都会经过审核。
此站点受 reCAPTCHA 保护,并且 Google 隐私政策和服务条款适用。