Have you ever wondered how people from different countries and cultures can communicate with each other without having to speak the same language? This type of communication is made possible through the use of translation devices. These fantastic tools have revolutionized our ability to bridge the gap between language barriers, allowing us to learn new languages, conduct international business conversations, and even navigate a foreign country in real-time. This blog post will delve into the history of these innovative translation devices and look at how far they've come over time – from primitive analog machines to sophisticated AI-powered tools.
Early Mechanical Translation Devices
The earliest attempts at language translation devices date back to the 17th century. Inventors like John Wilkins and Athanasius Kircher designed mechanical devices with rotating dials containing various words and phrases in different languages. Users would align the dials to form sentences in the target language. While these primitive machines could only produce a limited range of phrases and limited results, they were a precursor to the modern language translation devices we know today.
Phrase Books and Pocket Translators
In the 20th century, phrasebooks and pocket translators became popular travel tools. These books contained commonly used phrases and their translations in multiple languages. While these simple tools could be helpful for basic communication needs, they lacked accuracy and flexibility.
Electronic Translators
Electronic translators started appearing in the 1970s and 1980s with advancements in electronics. These devices had small screens and built-in databases of words and phrases. Users could input a word or phrase in one language, and the device would display the translation in another. Despite their limited capabilities, these devices provided a more convenient alternative to phrasebooks and pocket translators.
Pocket-Sized Translators
By the 1990s, pocket-sized electronic translators had become more sophisticated, featuring larger databases and improved accuracy. Some models even included voice input and output capabilities. These devices offered a more comprehensive translation experience, allowing travellers to communicate freely in foreign countries.
Mobile Apps and Software
The proliferation of smartphones in the 2000s led to the development of language translation apps. These apps could be downloaded onto smartphones, enabling users to access translation services. Companies like Google introduced translation apps that could translate spoken language and text in real-time.
Online Translation Services
Online platforms like Google Translate and Bing Translator gained popularity. These web-based services allowed users to enter text or even entire documents for translation. The quality of translation improved over time due to advancements in machine learning and AI.
Speech-to-Speech Translation
Modern translation devices started focusing on real-time speech translation. These devices, often in earbuds or small gadgets, could translate spoken language on the spot. They utilized machine learning algorithms and AI to provide more accurate and natural-sounding translations.
Integration of AI and Neural Networks
With the advent of neural machine translation and AI technologies, translation devices became even more accurate and context-aware. These systems could understand idiomatic expressions and nuanced language use, resulting in more fluid conversations.
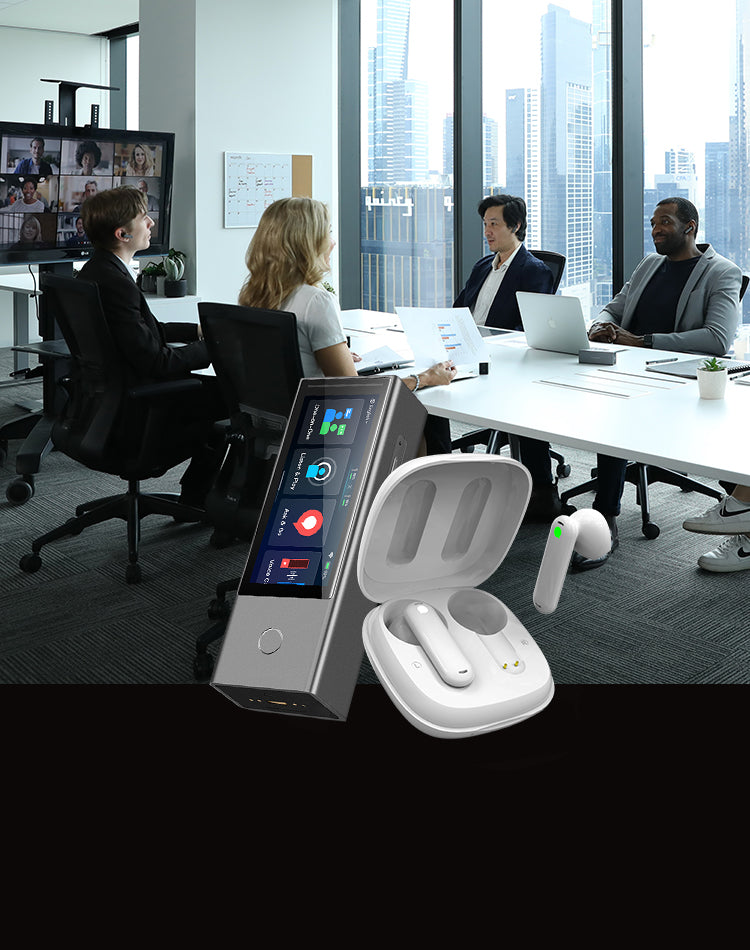
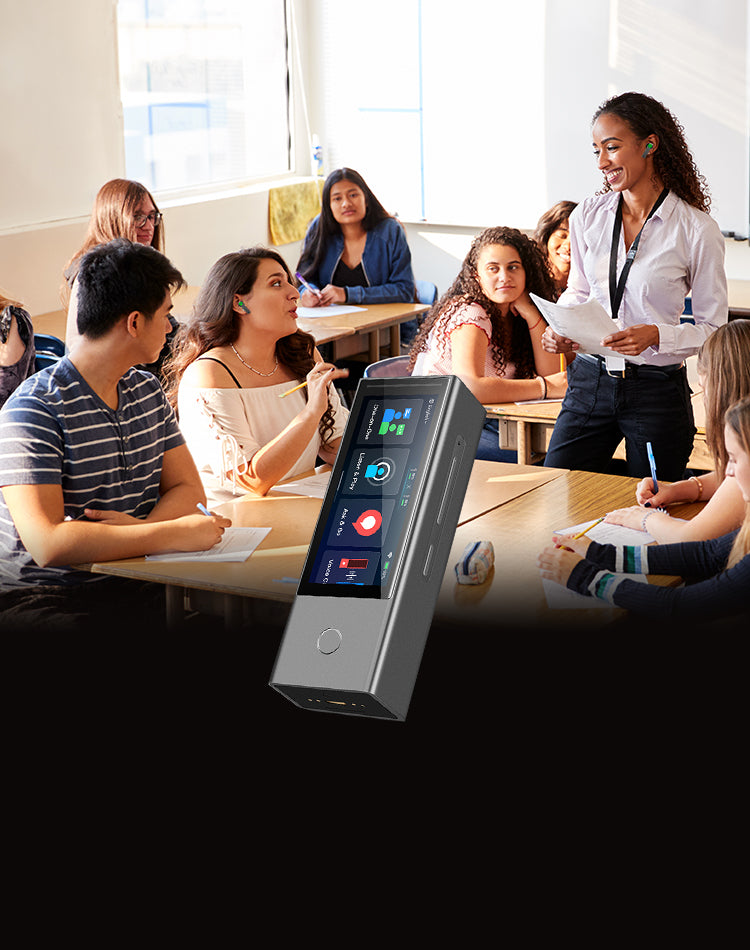
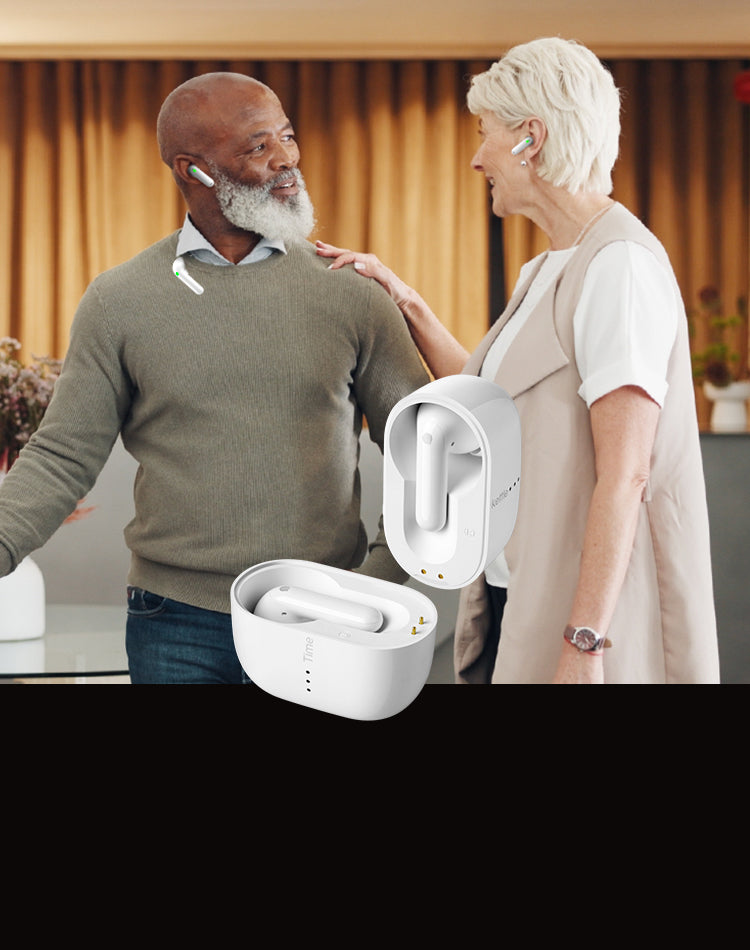
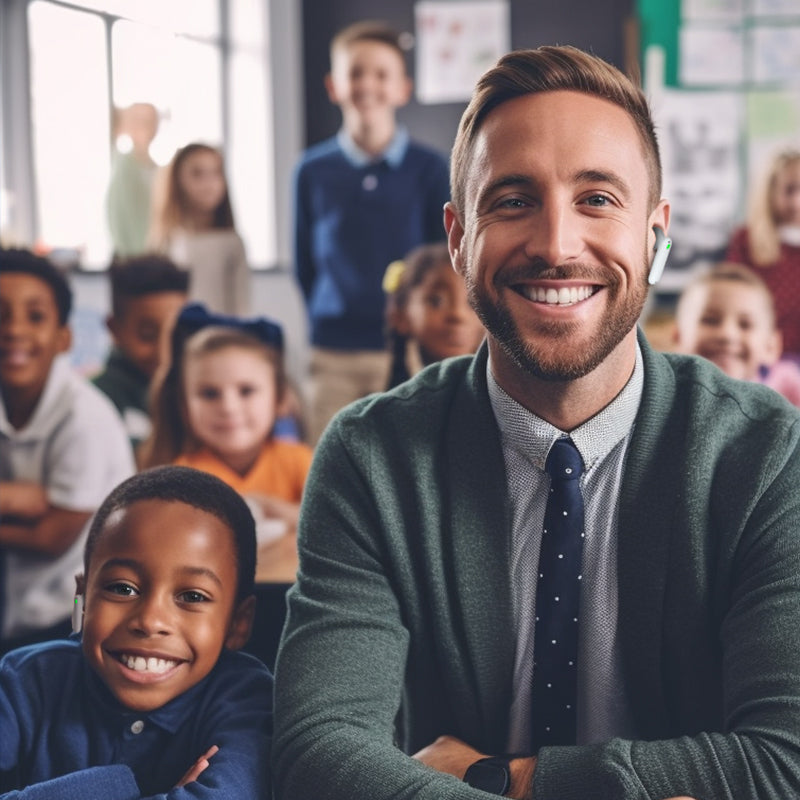
Smart Earbuds and Wearable Devices
Recent advancements have led to the development of smart earbuds equipped with real-time translation capabilities. These earbuds use AI to process spoken language and provide instant translations directly into the user's ear. They offer a convenient way for travellers to communicate without carrying bulky electronic translators.
Ongoing Improvements
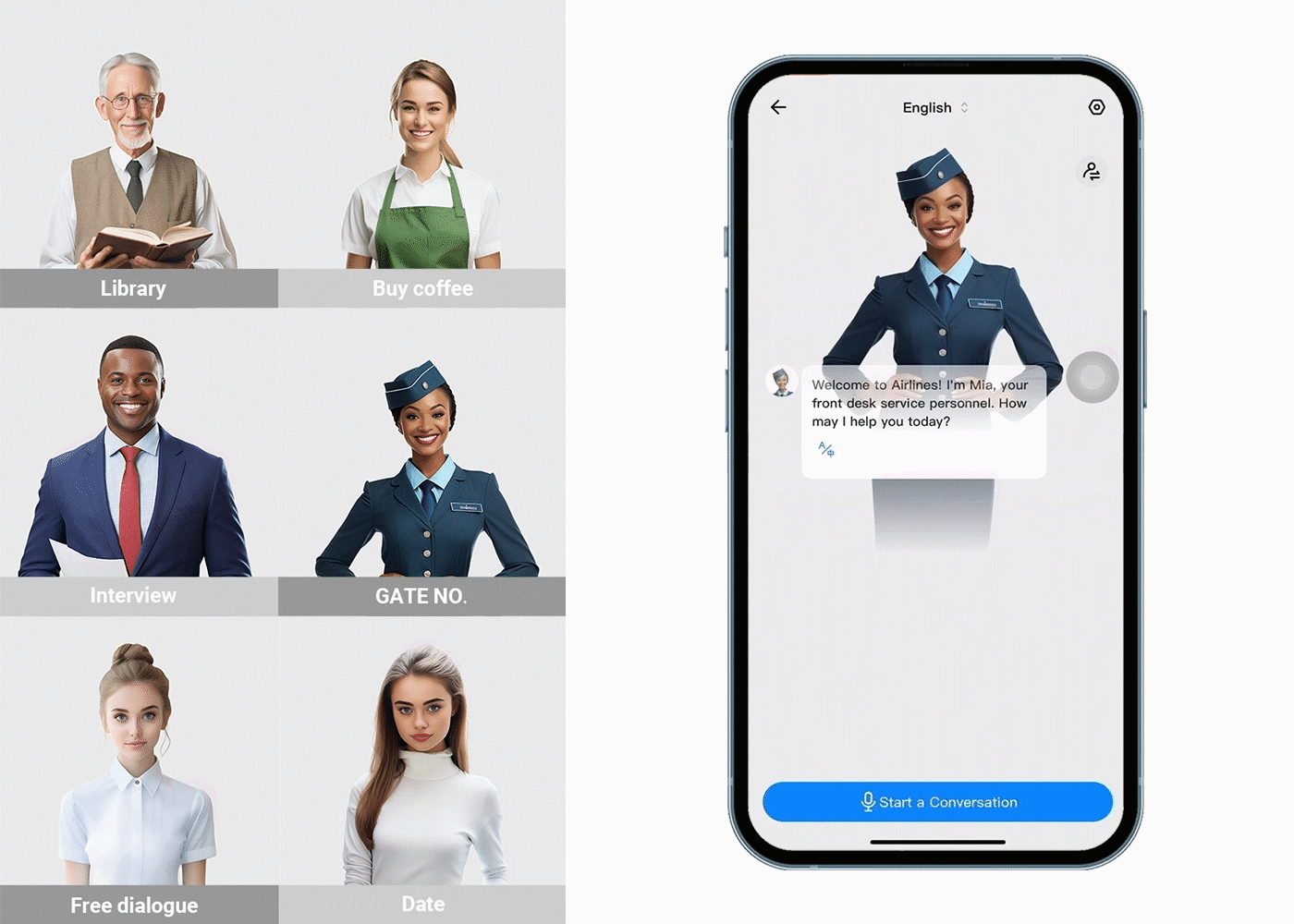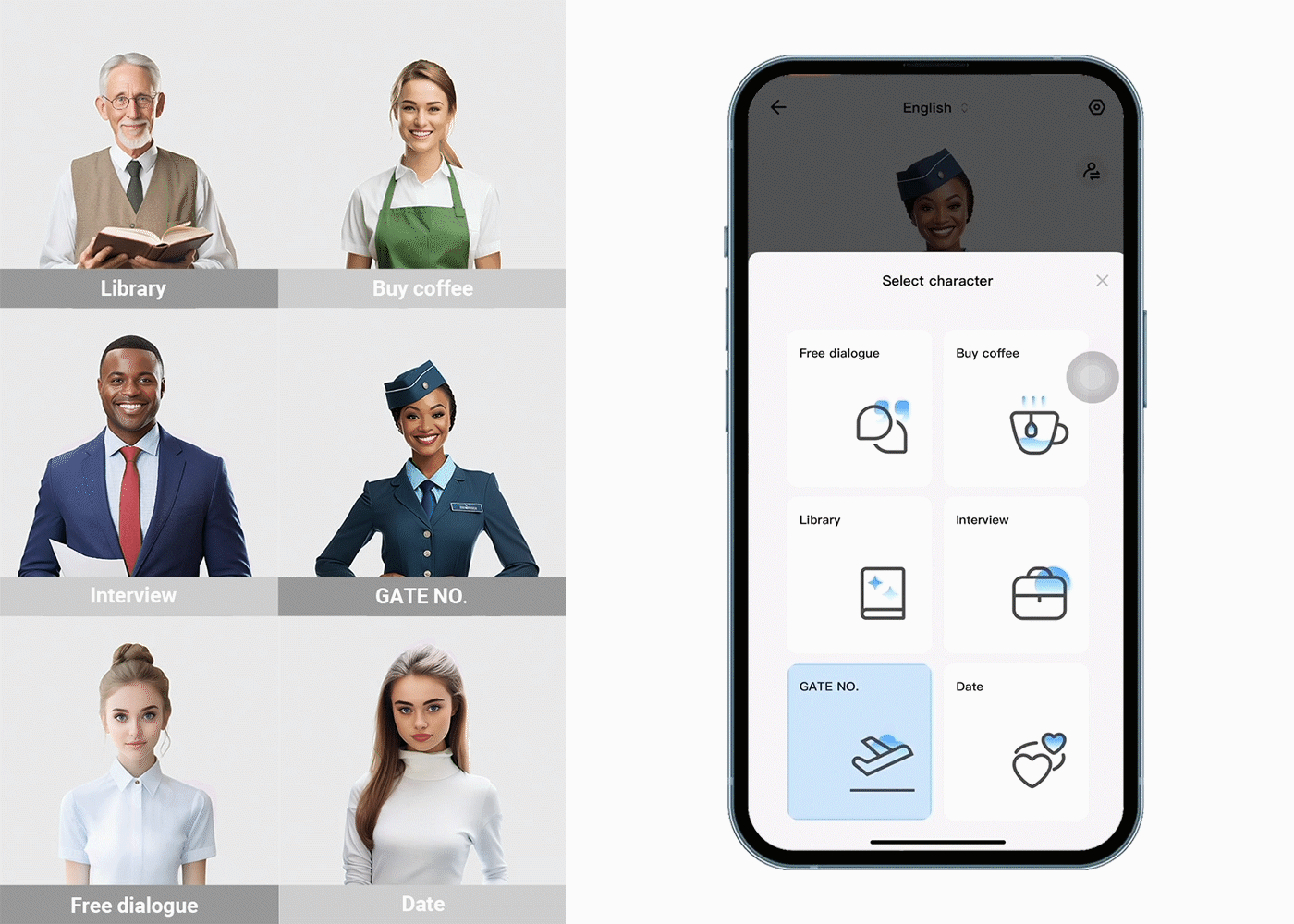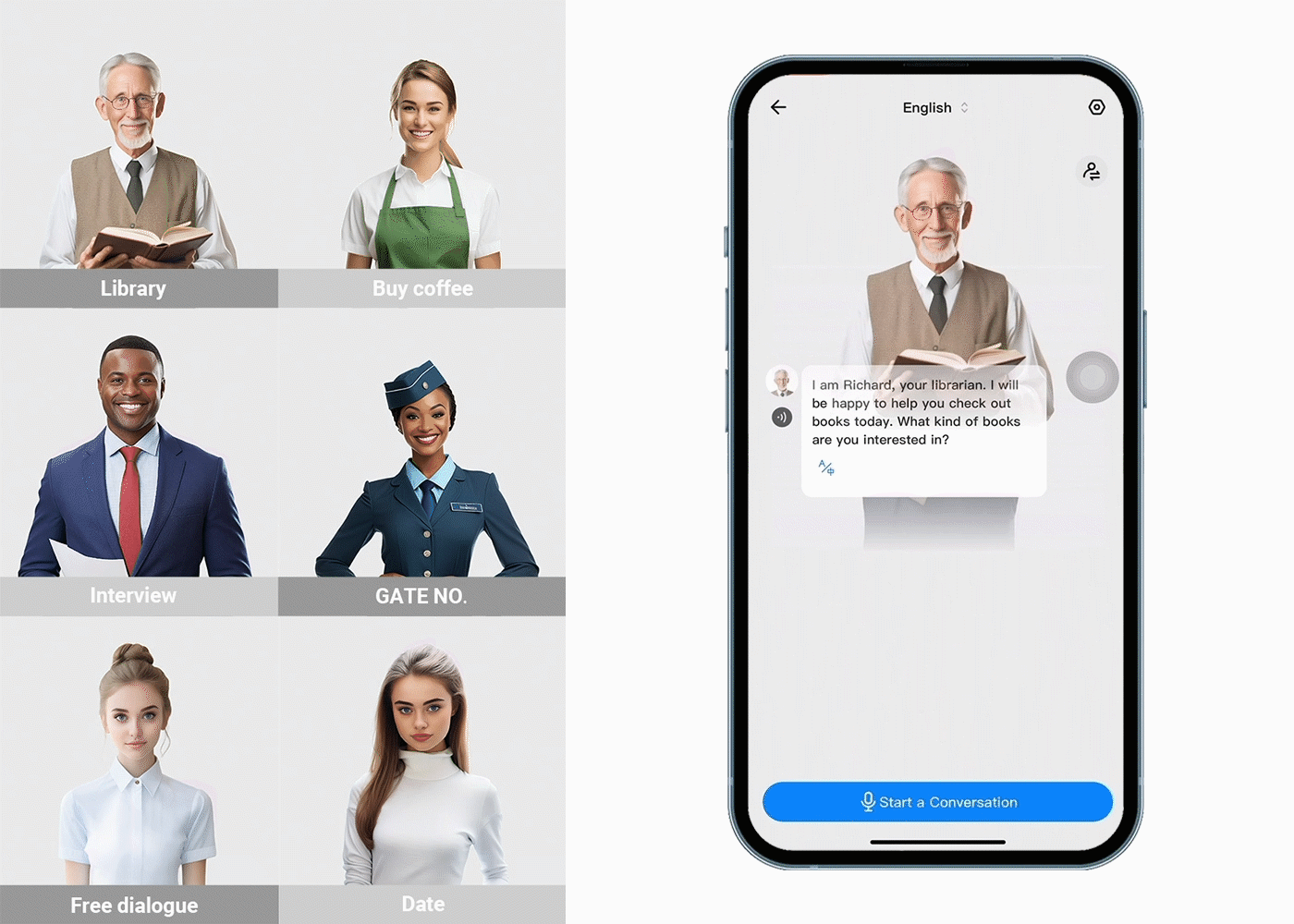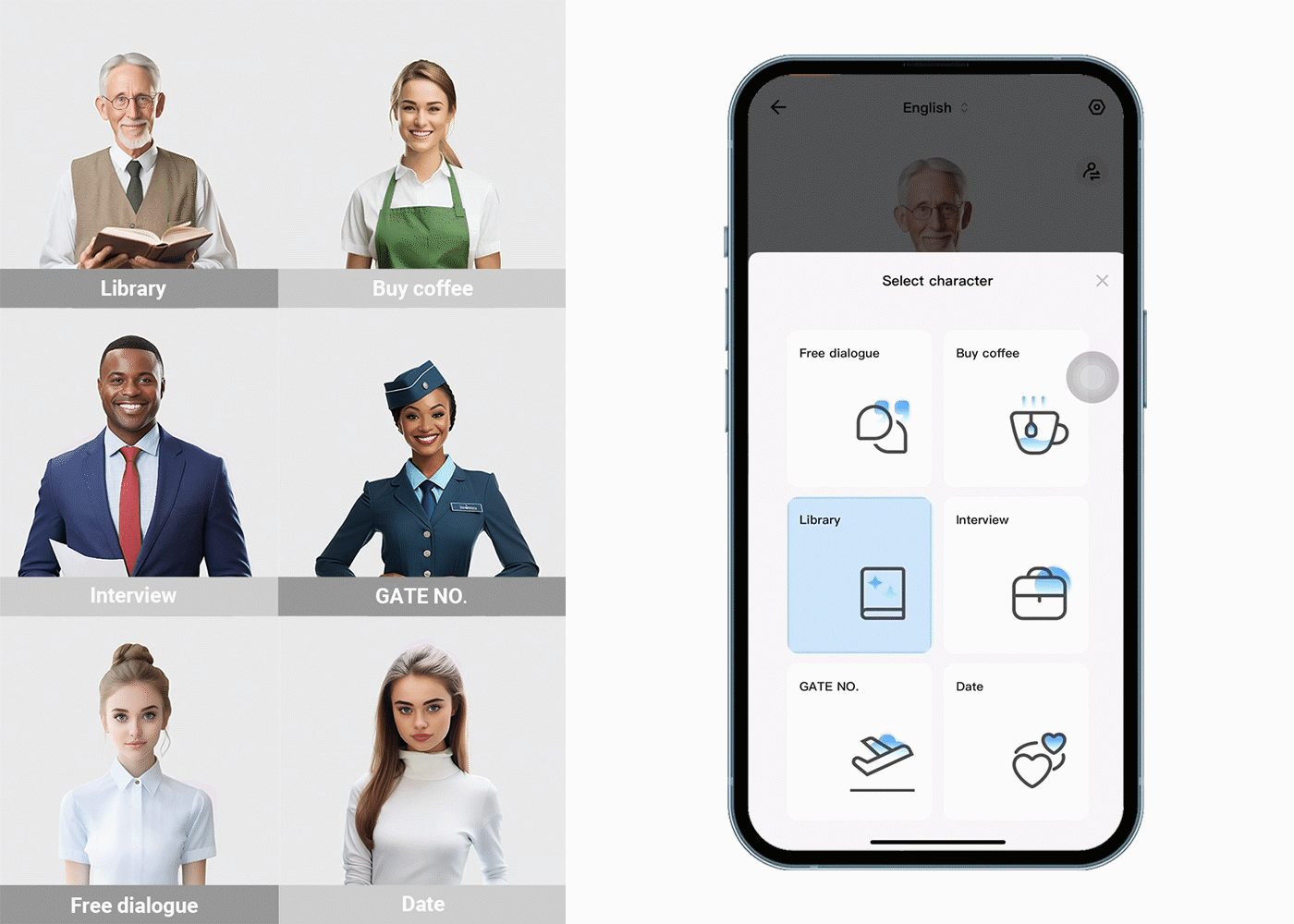
Translation gadgets are improving because of more innovative computer programs, better ways of understanding how people naturally speak, and machines that learn from experience. These improvements make translation gadgets more accurate, faster, and easier to use. As technology improves, there are new chances to make it even easier for people who speak different languages to talk to each other. The Timekettle Translator Earbuds are a great example of these gadgets. It is designed to help people talk to each other even if they don't speak the same language. When you wear these earbuds, the tiny microphones inside them listen to what people are saying, and then a computer quickly changes the words into a different language. The translated words come from the earbuds so you can understand each other without problems.
Features and Challenges
Language translation earbuds commonly offer features such as support for multiple languages, noise cancellation for improved speech recognition, and a comfortable fit for extended use. However, challenges remain, including accurately handling various dialects, accents, context-dependent phrases, and cultural nuances affecting translation accuracy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey of language translation devices shows how innovative thinking and a strong dedication to making communication easier have created something unique. We started with people translating languages, and now we have super-intelligent devices using AI to do it for us. These devices have changed the way the world talks and work together. As technology keeps improving, it's exciting to think about a future where language barriers won't be a problem anymore. This could bring people from everywhere even closer, understanding each other better.
 Talk to Customer Service 1(833) 491-1328
Talk to Customer Service 1(833) 491-1328





































댓글 남기기
모든 댓글은 게시 전 검토됩니다.
이 사이트는 hCaptcha에 의해 보호되며, hCaptcha의 개인 정보 보호 정책 과 서비스 약관 이 적용됩니다.